 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsApical ectodermal ridge induction is essential for tetrapod limb development. Which one of the following is NOT essential for the formation of a functional limb?
Tbx genes and Wnt
Androsterone
Apoptotic genes
Fibroblast growth factor
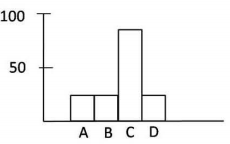
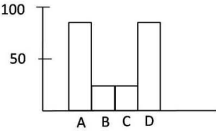
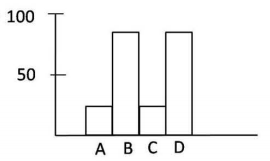
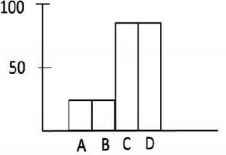
A protein X is kept in an inactive state in the cytosol as complexed with protein Y. Under certain stress stimuli, Y gets phosphorylated resulting in its proteasomal degradation. X becomes free, translocated to the nucleus, and results in the transcription of a gene that causes cell death by apoptosis. Stress stimuli were given to the following four different cases.
Case A: Protein Y has a mutation such that phosphorylation leading to proteasomal degradation does not occur.
Case B: Cells are transfected with a gene that encodes for a protein L that inhibits the translocation of protein Y to the nucleus.
Case C: Cells are transfected only with an empty vector used to transfected the gene for protein L.
Case D: Cells are treated with Z-VAD-FMK, a broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor.
Which one of the following graphs best describes the apoptotic state of the cells in the above cases? Y-axis represents % apoptotic cells.
Driesch performed the famous "pressure plate" experiment involving intricate recombination with an 8-celled sea urchin embryo. This procedure reshuffled the nuclei that normally would have been in the region destined to form endoderm into the presumptive ectoderm region. If segregation of nuclear determinants had occurred, the resulting embryo should have been disordered. However, Driesch obtained normal larvae from these embryos. The possible interpretation regarding the 8-celled sea urchin embryo are:
A. The prospective potency of an isolated blastomere is greater than its actual prospective fate.
B. The prospective potency and the prospective fate of the blastomere were identical.
C. Sea-urchin embryo is a "harmoniously equipotential system" because all of its potentially independent parts interacted together to form a single embryo.
D. Regulative development occurs where location of the cell in the ambryo determines its fate.
Which of the above interpretation(s) is/are true?
Only A
Only D
Only A and B
A, C, and D
Consider the following events which occur during fertilization of sea urchin eggs.
A. Resact/ Speract are peptides released from the egg jelly and help in sperm attraction.
B. Bindin, an acrosomal protein interacts in a species-specific manner with eggs.
C. A "respiratory burst" occurs during cross-linking of the fertilization envelope, where a calcium-dependent increase in oxygen levels is observed.
D. IP3, which is formed at the site of sperm entry, sequester calcium leading to cortical granule exocytosis.
Which of the above statement(s) is NOT TRUE?
Only C
A and C
Only D
B and D
Following statements were given regarding the decisions taken during the development of mammalian embryos:
A. The pluripotency of the inner cell mass (ICM) is maintained by a core of three transcription factors, Oct 4, Sox 2, and Nanog.
B. Prior to blastocyst formation each blastomere expresses both Cdx 2 and the Oct 4 transcription factors and appears to be capable of becoming either ICM or trophoblast.
C. Both ICM and trophoblast cells synthesize transcription factor Cdx2.
D. Oct 4 activates Cdx 2 expressions enabling some cells to become trophoblast and other cells to become ICM.
Which of the above statements are true?
A and B
A and C
B and D
B and C
Apoptosis during early development is essential for proper formation of different structures. In C. elegans, apoptosis is accentuated by ced-3 and ced-4 genes, which in turn are negatively regulated by ced-9 and eventually EGL-1. When compared to mammals, functionally similar homologues have been identified. Accordingly, which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
CED-4 resembles Apaf-1.
CED-9 resembles Bcl-XL
CED-3 resembles caspase-3.
CED-4 resembles caspase-9
Individual and overlapping expression of homeotic genes in adjacent whorls of a flower determine the pattern of floral organ development. In an Arabidopsis mutant, floral organs are distributed as follows:
Whorl 1 (outer most) - carpel
Whorl 2 - stamens
Whorl 3- stamens
Whorl 4 (inner most) - carpel
Loss of function mutation in which one of the following genes would have caused the above pattern of floral organ development?
APETALA 2
APETALA 3
PISTILLATA
AGAMOUS
Following are list of some proteins
A. BCL-2
B. BCL-XL
C. A1
D. BAX
Which of the protein(s) is/are NOT anti-apoptotic?
D only
C only
A and B only
B and D only
The dorsal-most vegetal cells of the amphibian embryo that is capable of inducing the organizer is called as Nieuwkoop centre and is marked by the presence of
Chordin
β-catenin
Goosecoid
Nanos
Which kind of cleavage is shown in mammals?
Holoblastic rotational
Meroblastic rotational
Holoblastic radial
Meroblastic radial
A.
Holoblastic rotational
Mammals show holoblastic cleavage.
