Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsSecondary xylem and phloem in dicot stem are produced by
Apical meristems
Vascular cambium
Axillary meristems
Phellogen
The term 'bark' refers to
Phellem, phelloderm and vascular cambium
Periderm and secondary xylem
Cork cambium and cork
Phellogen, phellem, phelloderm and Secondary phloem
What differentiates leaf of dicots from monocots?
Parallel venation
Differentiation of palisade and spongy parenchyma
Stomata only on upper side
Stomata both on upper and lower sides
Duramen is present in
inner region of secondary wood
part of sap wood
outer region of secondary wood
region of pericycle
Meristematic tissue in vascular bundle is
phellem
procambium
interfascicular cambium
fascicular cambium
Quiescent centre is the zone of
least mitotic activity in the root apex
least mitotic activity in the shoot apex
maximum mitotic activity in the root apex
maximum mitotic activity in the shoot apex
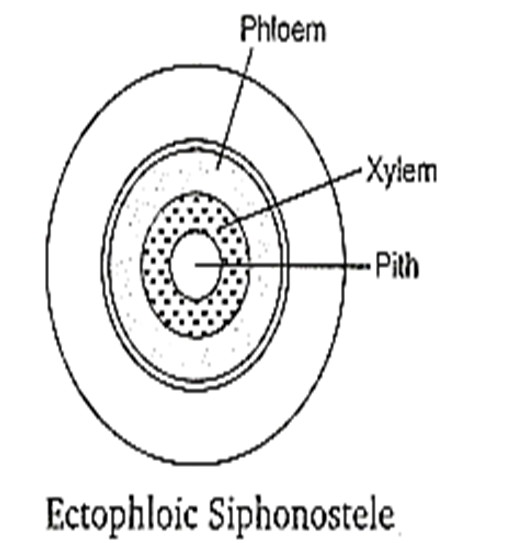
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in
Adiantum and Cucurbitaceae
Osmunda and Equisetum
Marsilea and Botrychium
Dicksonia and maiden hair fem
B.
Osmunda and Equisetum
In the ectophloic siphonostele the xylem surrounds pith and this xylem is surrounded by phloem, pericycle and endoderm is respectively.
eg, Osmunda and Equisetum.