Trace the effects of simultaneous shifts of demand and supply curves on equilibrium price and quantity.
or
Explain with the help of a diagram a situation when both demand and supply curves shift to the right but equilibrium price remains the sa
Effects of simultaneous demand and supply shifts (simultaneous change in demand and supply). Although there are many possibilities but we discuss its two main possibilities. (a) Effect of simultaneous increase in demand and supply (i.e., when demand and supply curves both shift rightward), and (b) Effect of simultaneous decrease in demand and supply.
(a) Effect of simultaneous rightward shift (i.e., increase) in demand and supply. There can be following three possibilities :
(i) When increase in supply is equal to increase in demand, equilibrium price will not change, i.e., the price will remain unaffected as shown in Fig. 4.14. In this case, since both demand and supply increase, therefore, both demand and supply curves shift to the right and since both increase in the same proportion, price remains unchanged but quantity increases from PE to PE1.
Fig. 4.14
(ii) When increase in supply is less than increase in demand, new equilibrium price will rise from OP to OP1 as shown in Fig. 4.15. Here equilibrium quantity will increase from PE to P1E1.
Fig. 4.15
(iii) When increase in supply is more than increase in demand, new equilibrium price will fall from OP to OP1 as shown in Fig. 4.16. Here equilibrium quantity will increase from PE to P1E1.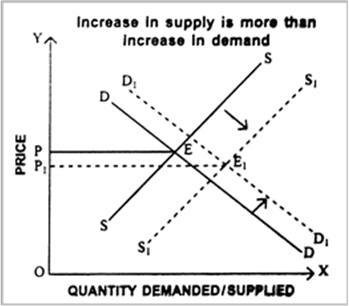
Fig. 4.16
(b) Effect of simultaneous leftward shift (i.e., decrease) in demand and supply. As discussed in part (a), we can analyse this situation in the similar manner. (i) When decrease in supply is equal to decrease in demand, the price will not be affected but the quantity will decrease in the same ratio. (ii) When decrease in supply is more than the one in demand, equilibrium price will increase and quantity will fall. (iii) When fall in supply is less than the fall in demand, equilibrium price will be less than the original price. The equilibrium quantity will fall.
Note : It is possible that the demand curve shifts rightwards and supply curve leftwards. In that case market price will definitely increase but quantity may increase or decrease. If demand curve shifts leftwards and supply rightwards, market price will decrease but quantity sold and purchased may increase or decrease.
Conclusion.
(i) Rightward shift (i.e., increase) in demand leads to increase in equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity whereas leftward shift (i.e., decrease) in demand results in fall in both equilibrium price and quantity.
(ii) Rightward shift (i.e., increase) in supply results in fall in price and rise in quantity. As against it, leftward shift (i.e., decrease) in supply gives rise to increase in price and fall in quantity.
(iii) Simultaneous rightward shift (increase) in both demand and supply. Its effect depends upon whether the increase in supply is equal to or more than or less than the increase in demand. However equilibrium quantity will definitely increase.
(iv) Simultaneous leftward shift (decrease) in demand and supply may lead to rise or fall in price or may not even affect the price depending upon the comparative rate of decrease in demand and supply. But the equilibrium quantity will fall definitely.