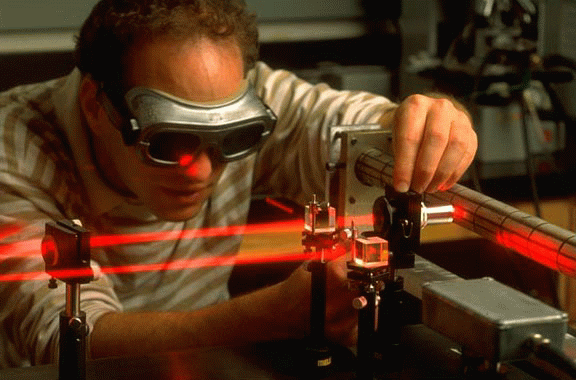
Lasers are devices that emit light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation.
The term “LASER” is an acronym for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation”
Laser light does not exist in nature. Only human technology can create laser light.
Unlike a regular light source, light from a laser contains exactly one color (wavelength) rather than a lot of different wavelengths. Laser light is therefore “monochromatic,” meaning of one color.
Laser light beams are very narrow and can be concentrated on one tiny spot. Laser light therefore is ‘collimated’.
Laser has a number of very special properties:
- It is usually emitted as a laser beam which can propagate over long lengths without much divergence and can be focused to very small spots.
- It can have a very narrow optical bandwidth, whereas e.g. most lamps emit light with a very broad optical spectrum.
- It may be emitted continuously, or alternatively in the form of short or ultrashort pulses, with durations from microseconds down to a few femtoseconds.
These properties make laser light very interesting for a range of applications.
- CD and DVD players.
- Bar code readers.
- Doctors use lasers to do delicate surgery, such as eye surgery.
- Lasers carry TV and telephone signals.
- Metal workers use lasers to cut and weld metal.
- Workers in clothing factories use lasers to cut through hundreds of layers of fabric at once.
Lasers are also finding many new uses in space missions. Lasers can be used in a device called a spectrometer.
A spectrometer uses light to identify the chemical composition of matter. As light passes through a gas, the gas soaks up certain colors, or wavelengths, of light. Different gases absorb different wavelengths. So the light that comes out the other side of a gas cloud will have a unique “fingerprint.” A spectrometer can read that fingerprint and identify the gas.
Simply want to say your article is as astounding. The clearness in your post is just great and i could
assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow
me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please carry on the enjoyable work.
opticals showrooms Many thanks another great posting. Where by in addition may anybody obtain that kind of information in this fantastic way with words? For sale business presentation in a month’s time, using this program . at the look for like info.
I do accept as true with every one of the ideas you might have displayed with your submit. There’re pretty genuine and will undoubtedly perform. However, your articles are way too swift to begin with.. color blindness test for kids free Could you desire stretch all of them a bit out of next time? Wanted submit.
Beneficial information and facts. Lucky me personally I found your site accidentally, using this program . astonished the key reason why this coincidence could not developed ahead of time! I actually saved as a favorite the idea..