CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
The smallest particle of an element, which may or may not have an independent existence, is called an atom, while the smallest particle of a substance which is capable of independent existence is called a molecule.
Molecules are classified as homoatomic and heteroatomic. Homoatomic molecules are made up of the atoms of the same element and heteroatomic molecules are made up of the atoms of the different elements having different atomicity (number of atoms in a molecule of an element) like monoatomic, diatomic, triatomic and polyatomic.
Atomic mass unit: One atomic mass unit is defined as a mass exactly equal to one-twelfth the mass of one carbon -12 atom. And 1 amu = 1.66056×10–24 g. Today, 'amu' has been replaced by 'u' which is known as unified mass.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass of an element is defined as the average relative mass of an atom of an element as compared to the mass of an atom of carbon -12 taken as 12.
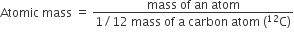
Gram atomic mass:
The quantity of an element whose mass in grams is numerically equal to its atomic mass. In simple terms, the atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is the gram atomic mass or gram atom.
For example, the atomic mass of oxygen = 16 amu
Therefore gram atomic mass of oxygen = 16 g
Many naturally occurring elements exist as more than one isotope.
The existence of these isotopes and their relative abundance (percent occurrence), the average atomic mass of that element can be computed. For example, carbon has three isotopes.
| Isotopes | Relative Abundance | Atomic mass (amu) |
| 12C | 98.892 | 12 |
| 13C | 1.108 | 13.00335 |
| 14C | 2 ×10–10 | 14.00317 |
The average atomic mass of carbon will come out to be :
(0.98892) (12 u) + ( 0.01108) (13.00335 u) + (2 × 10–12) (14.00317 u)
= 12.011 u
Sum of atomic masses of the elements present in one formula unit of a compound. It is used for the ionic compounds.
The molecular mass of a substance is defined as the average relative mass of its molecule as compared to the mass of an atom of C-12 taken as 12. It expresses as to how many times the molecule of a substance is heavier than 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon.
For example, a molecule of carbon dioxide is 44 times heavier than 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon. Therefore the molecular mass of CO2 is 44 amu. It is obtained by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms present in one molecule.
Molecular mass of methane,
(CH4) = (12.011 u) + 4 (1.008 u)
= 16.043 u