CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Motion can be measured in different ways i.e.,
Speed: A speed of a body is defined as the distance travelled by a body per unit time.

Speed is a scalar quantity.
SI Unit of speed ms-1
Uniform Speed: When a body travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, the speed of the body is said to be uniform.
Non-uniform Speed: When a body travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time, the speed of the body is said to be non-uniform.
Average speed: For non-uniform motion, the average speed will describe one single value of speed throughout the motion of the body.
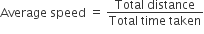
Velocity: Velocity of a body is the distance travelled by the body in unit time in a given direction.

Velocity is a vector quantity. Its value changes when either its magnitude or direction changes.
SI Unit of velocity ms-1
For non-uniform motion in a given line, average velocity will be calculated in the same way as done in average speed.
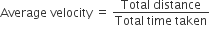
Average velocity: For uniformly changing velocity, the average velocity can be calculated as follows :

Here u = initial velocity
v = final velocity