CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
When an object moves along a straight line with uniform acceleration, it is possible to relate its velocity, acceleration during motion and the distance covered by it in a certain time interval by a set of equations known as the equations of motion. There are three such equations.
These are:
v = u + at
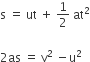
Graphical Derivation :
Suppose a body has initial velocity ‘u’ (i.e., the velocity at time t = 0 sec.) at
point ‘A’ and this velocity changes to ‘v’ at point ‘B’ in ‘t’ secs. i.e., final velocity will be ‘v’.

For such a body there will be an acceleration
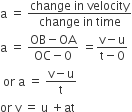
second Equation
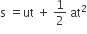
Distance travelled by object = Area of OABC (trapezium)
= Area of OADC (rectangle) + Area of ΔABD
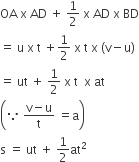
Third equation
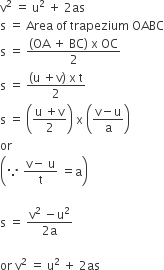
position time relation
Velocity -Time relation