CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Many times in the study of chemistry, one has to deal with experimental data as well as theoretical calculations. The measurement uncertainty is often taken as the standard deviation of a state-of-knowledge probability distribution over the possible values.
Dimensional Analysis During calculations generally there is a need to convert units from one system to other. This is called factor label method or unit factor method or dimensional analysis.
For example- 5 feet and 2 inches (height of an Indian female) is to be converted in SI unit:
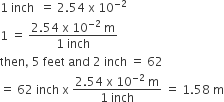
In which any number can be represented in form N × 10n (Where n is an exponent having positive or negative values and N can vary between 1 to 10). E.g. we can write 232.508 as 2.32508 x102 in scientific notation. Similarly, 0.00016 can be written as 1.6 x 10–4.
Precision refers to the closeness of various measurements for the same quantity.
Accuracy is the agreement of a particular value to the true value of the result.
The reliability of a measurement is indicated by the number of digits used to represent it. To express it more accurately we express it with digits that are known with certainty. These are called as Significant figures. They contain all the certain digits plus one doubtful digit in a number.
Rules for Determining the Number of Significant Figures
Retention of Significant Figures - Rounding off Figures