CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Properties of ideal solution which depends upon a number of particles of solute but independent of the nature of the particles are called colligative properties.
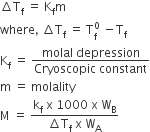
The excess pressure that must be applied to a solution side to prevent osmosis i.e. to stop passage of solvent molecules into it through a semi-permeable membrane.
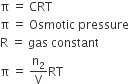
Here V is the volume of a solution in litres containing n2 moles of solute.If w2 grams of solute, of molar mass, M2 is present in the solution, then n2 = w2 / M2 and we can write,
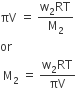
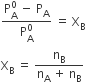
For dilute solution, nB<<nA, hence nB is neglected in the denominator.
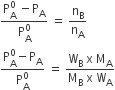
The phenomenon of reversal of the direction of osmosis by the application of a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure on the solution side is known as reverse osmosis. In this case, the pure solvent flows out of the solution through a semi-permeable membrane.
Reverse osmosis takes place only when external energy is applied to the more saline solution.
Reverse osmosis is used in the desalination of sea-water.