CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
When two (or more) bodies act upon one another, their total momentum remains constant (or conserved) provided no external forces are acting.
Initial momentum = Final momentum
Suppose, two objects A and B each of mass m1 and mass m2 are moving initially with velocities u1 and u2, strike each other after time t and start moving with velocities v1 and v2 respectively.

Now,
Initial momentum of object A = m1u1
Initial momentum of object B = m2u2
Final momentum of object A = m1v1
Final momentum of object B = m2v2
So, Rate of change of momentum in A,
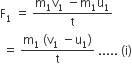
And Rate of change of momentum in B,
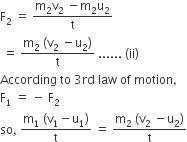
[From equations (i) & (ii)]
m1v1 – m2v2 = − m2v2 + m2u2
So, m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
Thus, Initial momentum = Final momentum