CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Ores that are mined from the earth are usually contaminated with a large number of impurities such as soil and sand etc.
Concentration or Dressing means, simply getting rid of as much of the unwanted rocky material as possible before the ore is converted into the metal. The impurities like clay are called gangue.
The physical methods adopted in dressing the ore (or) enriching the ore depends upon the difference between physical properties of ore and gangue.
Ores that are mined from the earth are usually contaminated with a large number of impurities such as soil and sand etc.
Concentration or Dressing means, simply getting rid of as much of the unwanted rocky material as possible before the ore is converted into the metal. The impurities like clay are called gangue.
The physical methods adopted in dressing the ore (or) enriching the ore depends upon the difference between physical properties of ore and gangue.
Metals low in the activity series are very unreactive.
The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heating alone.
For example, cinnabar (HgS) is an ore of mercury. When it is heated in air, it is first converted into mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is then reduced to mercury on further heating.
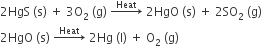
Metals are found in the earth’s crust in the free state. The metals at the bottom of the activity series are the least reactive. They are often found in a free state. For example, gold, silver, platinum and copper are found in the free state.
Copper and silver are also found in the combined state as their sulphide or oxide ores. The metals at the top of the activity series (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) are so reactive that they are never found in
nature as free elements.
The metals in the middle of the activity series (Zn, Fe, Pb, etc.) are moderately reactive. They are found in the earth’s crust mainly as oxides, sulphides or carbonates.

The earth’s crust is the major source of metals. Seawater also contains some soluble salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc. The elements or compounds, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are known as minerals.
Minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it. These minerals are called ores.