 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeState reasons for the following:
(i) pKb value for aniline is more than that for methylamine.
(ii) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not soluble in water.
(iii) Primary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines.The conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts is known as __________ .
Account for the following:
(i) Primary amines (R-NH2) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel - Crafts reactions:
(iii) (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
OR
(i) The greater the extent of intermolecular hydrogen bonding, greater is the boiling point of the compound. Primary amines are involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonding, whereas tertiary amines do not have any available hydrogen atoms, and hence they are not involved in any intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Thus, primary amines (R-NH2) have higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) A Friedel-Crafts reaction is carried out in the presence of a lewis acid such as AlCl3. Aniline being basic in nature reacts with AlCl3 to form a salt (as shown in the following equation).
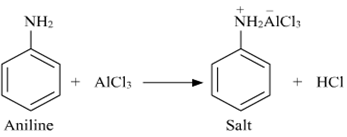
Due to the positive charge on the N-atom, electrophilic substitution in the benzene ring is deactivated. Hence, aniline does not undergo the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(iii) The order of basic strength of aliphatic amines in the aqueous phase, is based on following factors:
Steric factor: Alkyl group is larger than hydrogen atom that causes steric hindrance to attack of acid. As the number of alkyl group increases from primary to tertiary. The steric hindrance also increases in the same direction.
Solvation of ions: when amines are dissolved in water, they form hydrogen bonds with a water molecule and release hydration energy; in the process converting themselves to the protonated amines to get stabilized. Greater the extent of hydrogen bonding, greater is the hydration energy released and more is the stability of the protonated amine; thus greater is the tendency of the amine to form cation leading to the greater basic strength of the amine. So, the actual order of basic strength in aqueous phase is found to be:
Secondary > Tertiary > Primary
Therefore, secondary amines are the strongest base in aqueous solution.
Give reasons :
Although –NH2 is o/p directing group, yet aniline on nitration gives a significant amount of m-nitroaniline.
