 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDefine enzymes. How do enzymes differ from ordinary chemical catalysts? Comment on the specificity of enzyme action. What is the most important reason for their specificity? Explain the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
What are the building blocks (repeat units) of proteins? Describe the structure of protein.
A protein is a high polymer on hydrolysis it yields amino acids. Thus, amino acids are the monomeric units of all proteins. In a molecule of protein, the amino acid residues are joined by peptide bonds. Therefore, proteins are also called condensation products of amino acids or polyamide.
Structure of proteins: (a) Primary structure: Primary structure is the combination of amino acids in a proper sequence through peptide bonds.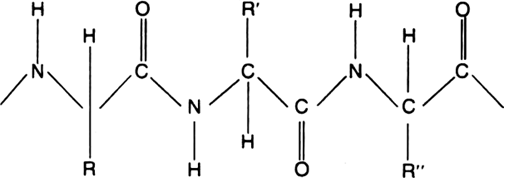
(b) Secondary structure: In many proteins, polypeptide chain gets coiled up to form α-helix which is right handed and is called α-helix. In the helix each NH group is hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl oxygen of the third amino acids residue from it. It is this hydrogen bonding between different parts of the same chain which holds the helix together. Some proteins have β-pleated structure. This is also called β-sheet structure. In the sheet arrangement two peptide chains lie side by side and are joined via hydrogen bonds.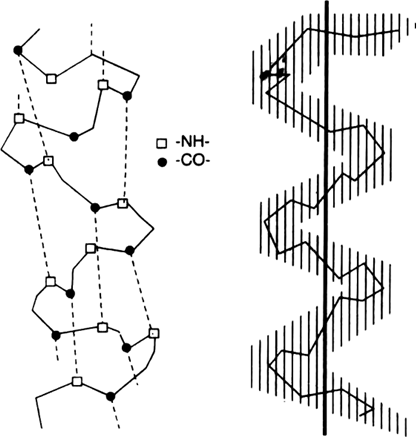
Fig. (a) Helical structure (b) The peptide
backbone in a helical structure.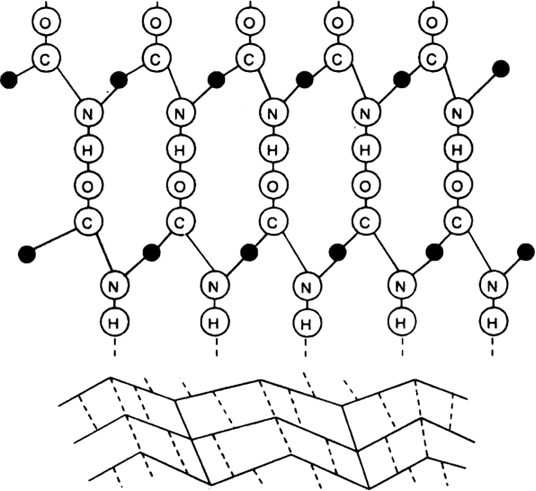
Fig. β-pleated sheet structure of a protein
(c) Tertiary structure: The peptide chains with its secondary may be further folded and twisted about itself forming many structural coils of diverse sizes or shapes. They, brings some distant amino acids residues close to each other. Tertiary structures are held and stabilized by : (i) hydrophobic interactions, (ii) hydrogen bonds, (iii) Van der Waals forces and (iv) disulphide linkages between two side chains.
(d) Quaternary structure: This defines the degree of polymerization of protein unit. Both fibrous and globular proteins may contain one or more polypeptide chains. In case of fibrous protein these are called monomeric while in case of globular these are referred to as oligomeric. The individual peptide chains of an oligomeric protein are called promoters. These promoters may be same or different but are held together by weak binding force.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Fill In the Blanks
Fill In the Blanks