 Short Answer Type
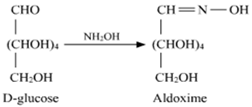
Short Answer Type(i) Write the product obtained when D-glucose reacts with H2N - OH.
(ii) Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why?
(iii) Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
(i) When D-glucose reacts with NH2OH, an aldoxime is formed.
(ii) In aqueous solutions, the carboxyl groups of amino acids lose a proton. Amino groups of amino acids, on the other hand, accept a proton, giving rise to a dipolar ion known as zwitter ion.
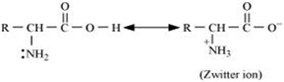
This is neutral, but contains both positive and negative charges. In the zwitter ionic form, amino acids show amphoteric behaviour as they react with both acids and bases.
(iii) Vitamin C is water soluble and is readily excreted in urine. Hence, it cannot be stored in our body.
Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely ‘anaemic’. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mrs. Anuradha supported her financially to get the medicines. After a month, Shanti was diagnosed to be normal.
(i) What values are displayed by Mrs. Anuradha?
(ii) Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes ‘pernicious anaemia’.
(iii) Give an example of a water soluble vitamin.
Write a reaction which shows that all the carbon atoms in glucose are linked in a straight chain.
Define the following as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
(i) Write the name of two monosaccharides obtained on hydrolysis of lactose sugar.
(ii) Why Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body?
(iii) What is the difference between a nucleoside and nucleotide?
i) Write the structural difference between starch and cellulose.
ii) What type of linkage is present in Nucleic acid ?
iii) Give one example each for fibrous protein and globular protein.
Write the main structural difference between DNA and RNA. Of the four bases, name those which are common to both DNA and RNA.
Write such reactions and facts about glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
