 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDefine the following terms as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
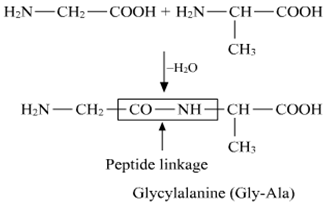
(i) Peptide linkage: It is the amide formed between the −COOH and −NH2 groups of two amino acid molecules.
(ii) Primary structure of proteins: Proteins contain one or more polypeptide chains and each chain has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids represents the primary structure of proteins.
(iii) Denaturation: It is the loss of biological activity of proteins because of some physical changes like changes in pH and temperature, due to which the unfolding of globules and the uncoiling of helix take place.
Examples: Coagulation of egg white on boiling and curdling of milk.
After watching a programme on TV about the presence of carcinogens(cancer causing
agents) Potassium bromate and Potassium iodate in bread and other bakery products, Ritu a class XII student decided to aware others about the adverse effects of these carcinogens in foods. She consulted the school principal and requested him to instruct canteen contractor to stop selling sandwiches, pizza, burgers and other bakery products to the students. Principal took an immediate action and instructed the canteen contractor to replace the bakery products with some proteins and vitamins rich food like fruits, salads, sprouts etc. The decision was welcomed by the parents and students.
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions :
(i) What are the values (at least two) displayed by Ritu?
(ii) Which polysaccharide component of carbohydrates is commonly present in bread?
(iii) Write the two types of secondary structure of proteins.
(iv) Give two examples of water soluble vitamins.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsOne mole of stachyose on hydrolysis yields
1 mole of glucose+ 1 mole of fructose+ 2 mole of galactose
2 mole of glucose + 1 mole of fructose + 1 mole of galactose
1 mole of glucose+ 2 mole of fructose+ 1 mole of galactose
2 mole of glucose+ 2 mole of fructose
