 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the orbital shapes of the following covalent molecules:
(i) HF (ii) H2O (iii) NH3.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeUsing the orbital overlap concept, explain the formation of:
(i) O2 molecule            (ii) N2 molecule.
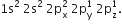
 -bond.
-bond. a bond. 
a bond. 
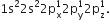  It has three half filled 2p-orbitals in its valence shell. In the formation of the nitrogen molecule, one of the three half-filled 2p orbitals of each nitrogen atom overlaps mutually along the internuclear axis to form a bond. The other two 2p-half filled orbitals of a nitrogen atom undergo sidewise overlapping with their parallel oriented 2p-orbitals of other nitrogen to form two
 It has three half filled 2p-orbitals in its valence shell. In the formation of the nitrogen molecule, one of the three half-filled 2p orbitals of each nitrogen atom overlaps mutually along the internuclear axis to form a bond. The other two 2p-half filled orbitals of a nitrogen atom undergo sidewise overlapping with their parallel oriented 2p-orbitals of other nitrogen to form two   bonds. Thus, two nitrogen atoms are linked together by a triple bond, one of which is sigma bond and the other two are
 bonds. Thus, two nitrogen atoms are linked together by a triple bond, one of which is sigma bond and the other two are   bonds.
 bonds.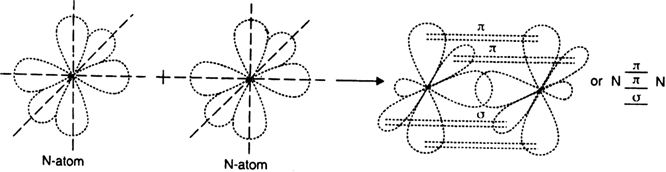
What is coordinate or dative bond? Explain the formation of the bond with some examples.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type