 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe half-life period of a first order reaction having rate constant k = 0.231 × 10-10 s-1 will be
32 × 1010 s
2 × 1010 s
3 × 1010 s
2 × 10-10 s
For the reaction X → Y, the concentrations of 'X' are 1.2 M, 0.6 M, 0.3 Mand 0.15 M at 0, 1, 2 and 3 hours respectively. The order of the reaction is
zero
half
one
two
C.
one
For the reaction, concentration of x are
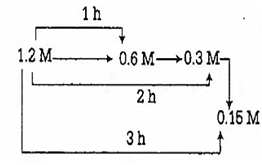
So, half-life(t1/2) = 1h
Therefore, order of the reaction is 'one'.
In a reaction, 2A + B → 3C, the concentration of A decreases from 0.5 mol L-1 to 0.3 mol L-1 in 10 minutes. The rate of production of 'C' during this period is
0.01 mol L-1 min-1
0.04 mol L-1 min-1
0.05 mol L-1 min-1
0.03 mol L-1 min-1
Ammonium ion (NH4+) reacts with nitrite ion (NO) in aqueous solution according to the equation
NH4+ (aq) + NO (aq) → N2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
The following initial rates of reaction have been measured for the given reactant concentrations.
| Expt. No. | [NH4+], (M) | [NO), (M) | Rate (M/hr) |
| 1 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| 2 | 0.015 | 0.020 | 0.030 |
| 3 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.005 |
Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction?
Rate = k[NH4+][NO]4
Rate = k [NH][NO]
Rate = k [NH][NO]2
Rate = k[NH]2[NO]
The work function of a metal is 5 eV. What is the kinetic energy of the photoelectron ejected from the metal surface if the energy of the incident radiation is 6.2 eV? (1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19)
1.92 × 10-19 J
6.626 × 10-19 J
8.10 × 10-19 J
1.92 × 10-18 J
The change in potential of the half-cell Cu2+|Cu when aqueous Cu2+ solution is diluted 100 times at 298 K?
increases by 120 mV
decreases by 120 mV
increases by 60 mV
decreases by 60 mV
The reaction, A + B → products is first order with respect to A and second order with respect to B. When 1.0 mole each of A and B were taken in one litre flask, the initial rate of the reaction is 1.0 × 10-2 mol L-1 s-1. The rate of the reaction when 50% of the reactants have been converted into products is
1.00 × 10-3 mol L-1 s-1
0.05 × 10-2 mol L-1 s-1
1.25 × 10-3 mol L-1 s-1
4.00 × 10-2 mol L-1 s-1
For the following reaction,
NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g)
the rate law is Rate = k [NO2]2. If 0.1 mole of gaseous carbon monoxide is added at constant temperature to the reaction mixture which of the following statement is true?
Both k and the reaction rate remain the same
Both k and the reaction rate increase
Both k and the reaction rate decrease
Only k increases, the reation rate remain the same
The rate constant and half-life of a first order reaction are related to each other as
t1/2 = 0.693 k
k = 0.693 t1/2
