 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsObserve the following reaction 2A + B → C. The rate of formation of C is 2.2 × 10-3 mol L-1min-1. What is the value of - (in mol L-1min-1)?
2.2 × 10-3
1.1 × 10-3
4.4 × 10-3
5.5 × 10-3
The rate constant of a first order reaction at 27°C is 10-3 min-1. The temperature coefficient of this reaction is 2. What is the rate constant (in min-1 ) at 17°C for this reaction ?
10-3
5 × 10-4
2 × 10-3
10-2
What is the temperature at which the kinetic energy of 0.3 moles of helium is equal to the kinetic energy of 0.4 moles of argon at 400 K?
400 K
873 K
533 K
300 K
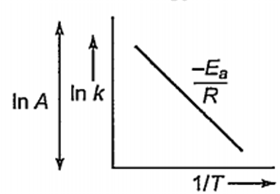
What is the slope of the straight line for the graph drawn between ln k and 1/T, where k is the rate constant of a reaction at temperature T?
-Ea/ 2.303R
-Ea/R
Ea/R
R/Ea
B.
-Ea/R
Arrhenius equation is = k = Ae-Ea/RT
On taking log both sides,
Electrons with a kinetic energy of 6.023 × 104 J/mol are evolved from the surface of a metal, when it is exposed to radiation of wavelength of 600 nm. The minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron from the metal atom is
2.3125 × 10-19 J
3 × 10-19 J
6.02 × 10-19 J
6.62 × 10-34 J
For a first order reaction at 27°C, the ratio of time required for 75% completion to 25% completion of reaction is
3.0
2.303
4.8
0.477
At T (K), the ratio of kinetic energies of 4g of H2 (g) and 8 g of O2 (g) is
1 : 4
4 : 1
2 : 1
8 : 1
Which one ofthe following statements is correct for the reaction?
CH3COOC2H5(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa (aq) + C2H5OH (aq)
Order is two but molecularity is one
Order is one but molecularity is two
Order is one but molecularity is one
Order is two but molecularity is two
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant decrease from 0.6 M to 0.3 M in 15 min. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in minutes is
14
12
30
3
