 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhich of the following pairs of elements would you expect to have lower first ionisation enthalpy? Explain your answer:
(a) Cl or F
(b) Cl or S
(c) K or Ar
(d) Kr or Xe.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAmong the elements of second period i.e. from Li to Ne, pick out the elements:
(a) with the highest first ionisation enthalpy
(b) with the highest electronegativity
(c) with the largest atomic radius
(d) which is the most reactive non-metal
(e) which is the most reactive metal ?
The first (IE1) and second (IE2) ionisation enthalpies (kJ mol-1) of a few elements by Roman numerals are as shown:
| IE1 | IE2 | |
| i | 2372 | IE2 |
| ii | 520 | 7300 |
| iii | 900 | 1760 |
| iv | 1680 | 380 |
which of the above elements is likely to be:
(i) a reactive metal
(ii) a reactive non-metal
(iii) a noble gas
(iv) a metal that forms a stable binary halide of the formula AX3 (X = halogen).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe IE1, of carbon, is more than that of boron while its IE2 value is smaller. Explain.
IE1 of carbon and boron:
It is primarily due to:
(i) the increase in nuclear charge.
(ii) The decrease in the atomic size of carbon. Due to the combined effect of these two factors, the force of attraction between the nucleus and the electron to be removed increases. Hence IE, value of carbon is more than that of boron.
IE2 of carbon and boron:
The electronic configuration of B+ and C+ ions are:
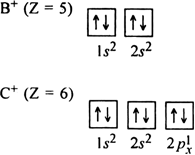
The electronic configuration of B+ ion is more symmetrical than that of C+ ion since in the former case, both the orbitals are filled. Therefore, the configuration of B+ ion is more stable and its IE2 value is more than that of C+ ion.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange the following in order of increasing ionisation enthalpies and assign reason:
(i) K+, Ar, Cl-
(ii) Fe, Fe2+, Fe3+
How would you explain the fact that the first ionization enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionization enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
The first ionization enthalpy values (in kJ mol-1) of group 13 elements are:
B Al Ga In Tl
801 577 579 558 589
How would you explain this deviation from the general trend?
