 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat is spectrochemical series? Explain the difference between a weak field ligand and a strong field ligand.
Bonding in [FeF6]3–
The oxidation state of Fe is +3 and its coordination number is 6. The complex has octahedral geometry and experimental study shows that it is paramagnetic.
The bonding in this entity is explained on the basis of overlap of sp3d2 hybrid orbitals of Fe3+ ion and six lone pair orbitals of cyanide ligands. Five 3d electrons are unpaired which make it paramagnetic. The outer electronic configuration of Fe3+ ion is 3d5 which is highly stable and no pairing of electrons takes place in presence of weak field of F– ions. Here, 4d–orbitals of Fe3+ (which are empty) are involved.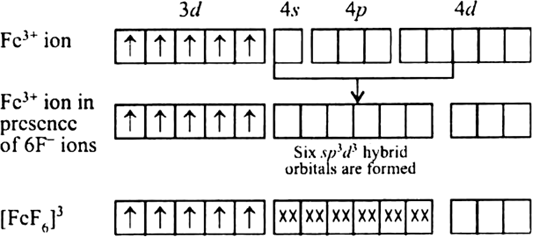
The entity is strongly paramagnetic due to five unpaired electrons and is an outer orbital complex.
