 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeUsing valency bond approach predict the shape and magnetism (paramagnetic or diamagnetic) of [Ni(CN)4]–.
Explain the following terms: (i) Inner orbital complex and (ii) outer orbital complex.
Deduce the structures of [NiCl4]2– and [Ni(CN)4]2– considering the hybridization of the metal ion. Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only) of the species.
NiCl42-, there is Ni2+ ion, However, in presence of weak field Cl- ligands, NO pairing of d-electrons occurs. Therefore, Ni2+ undergoes sp3 hybridization to make bonds with Cl- ligands in tetrahedral geometry. As there are unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals, NiCl42- is paramagnetic. 
Since it have two unpaired electron electron therefore the magnetic moment :
In [Ni(CN)4]2-, there is Ni2+ ion for which the electronic configuration in the valence shell is 3d8 4s0.
In presence of strong field CN- ions, all the electrons are paired up. The empty 4d, 3s and two 4p orbitals undergo dsp2 hybridization to make bonds with CN- ligands in square planar geometry. Thus [Ni(CN)4]2- is diamagnetic. 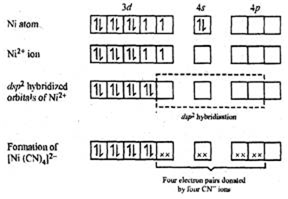
Since there is no any unpaired electron therefore its magnetic moment is zero.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIllustrate with an example each of the following terms: (i) Ionization isomerism, (ii) coordination isomerism, (iii) Linkage isomerism, (iv) Geometrical isomerism (v) Optical isomerism.
Draw the isomers of each of the following:
(i) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (ii) [PtCl3Br3]2–
(ii) [Co(NH3)4Cl2] (iv) [Co(en)2Cl2]+.
