 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the effect of adding an inert gas(say He or N2):
(i) at constant volume and
(ii) at the constant pressure on the following equilibrium:![]()
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type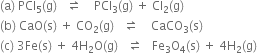
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhich of the following reactions will get affected by increasing the pressure? Also, mention whether the change will cause the reaction to go into forward or backward direction?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type
The change of ice into water is a reversible endothermic (i.e. accompanied by absorption of heat) process. The reaction involves a decrease in volume. Hence according to Le-Chatelier’s principle:
(i) With the increase in pressure: The equilibrium tends to shift in that direction in which there occurs a decrease in the volume. So in this case, an increase in pressure favours the conversion of ice into water.
(ii) With the increase in temperature: The equilibrium shifts to the right i.e. towards the direction in which heat is absorbed. Thus, increase in temperature favours melting of ice.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDescribe the effect of:
(a) addition of H2
(b) addition of CH3OH
(c) removal of CO
(d) removal of CH3OH
on the equilibrium of the reaction:
![]()
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type