 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) write the expression for the equilibrium constant for the reaction;
(ii) at room temperature (300 K) will Kp be greater than, less than or equal to Kp at 900 K;
(iii) how will the equilibrium be affected if the volume of the vessel containing the three gases is reduced, keeping the temperature constant; what happens;
(iv) what is the effect of adding 1 mole He(g) to a flask containing SO2,O2 and SO3 at equilibrium at constant temperature?

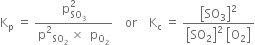
The dissociation of phosgene is represented as follows:![]()
When the mixture of these three gases is compressed at constant temperature, what happens to:
(i) the amount of CO in the mixture.
(ii) the partial pressure of COCl2
(iii) the equilibrium constant for the reaction?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFor the equilibrium ![]() the value of the equilibrium constant KC is
the value of the equilibrium constant KC is ![]() Calculate Kp for the reaction at this temperature.
Calculate Kp for the reaction at this temperature.
For the equilibrium![]()
the value of the constant, Kc is ![]() Calculate
Calculate ![]() for the reaction at this temperature.
for the reaction at this temperature.
The value of Kc for the reaction  is found to be 186.9 at 750K. Calculate the value of
is found to be 186.9 at 750K. Calculate the value of ![]() if partial pressures are expressed in bars.
if partial pressures are expressed in bars.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe equilibrium constant at 278K for ![]() is
is ![]() . In a solution in which copper has displaced some silver ions from the solution, concentration of Cu2+ ions is 1.8 x 10-2 mol L-1 and the concentration of Ag+ ions is 3·0 ×10–9 mol L–1. Is the system at equilibrium?
. In a solution in which copper has displaced some silver ions from the solution, concentration of Cu2+ ions is 1.8 x 10-2 mol L-1 and the concentration of Ag+ ions is 3·0 ×10–9 mol L–1. Is the system at equilibrium?
