 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIf 20 ml of 1·5 × 10–5 M BaCl2 solution is mixed with 40 ml of 0·9 × 10–5MNa2SO4 solution, will a precipitate get formed? Ksp for BaSO4 = 0·1 × 10–10.
If 25.0 cm3 of 0.50 M - Ba(NO3)2 are mixed with 25·0 cm3 of 0·0220M-NaF, will any BaF2 precipitate [Ksp of Ba F2 is 1·7 × 10–6 at 298 K.]
Equal volumes of 0.002M solutions of sodium iodate and cupric chlorate are mixed together. Will it lead precipitation of copper iodate? (For cupric iodate Ksp = 7·4 × 10–8).
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe concentration of sulphide ion in 0·1M HCl solution saturated with hydrogen sulphide is 1·0 × 10–19M. If 10 mL of this solution is added to 5 mL of 0·04M solution of FeSO4, MnCl2, ZnCl2 and CaCl2, in which solutions precipitation will take place? Given Ksp for FeS = 6·3 × 10–18, MnS = 2·5 × 10–13, ZnS =1·6 × 10–24and CdS = 8·0 × 10–27.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe values of Ksp of two sparingly soluble salts Ni(OH)2 and AgCN are 2·0 × 10–15 and 6 × 10–17 respectively. Which salt is more soluble ? Explain
The solubility product constant of Ag2CrO4 and AgBr are 1·1 × 10–12 and 5·0 × 10–13 respectively. Calculate the ratio of the molarities of their saturated solutions.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeFlow will you purify an impure sample of sodium chloride containing water soluble impurities?
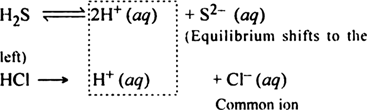
Due to common ion effect of H+ ions, the degree of dissociation of H2S is suppressed, so the concentration of sulphide ions decreases. Thus the ionic product of sulphides of group II cations (Hg2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Bi3+) decreases. But this is large enough to exceed the value of their solubility products and radicals of group II get precipitated.
Other groups cations are not precipitated because their Ksp are comparatively higher.
