 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAn organic compound ‘A’ having the molecular formula C4H8 on treatment with dilute sulphuric acid give another compound ‘B’. B on treatment with conc. HCl and anhydrous zinc chloride gives ‘C’. C on treatment with sodium ethoxide gives back ‘A’. Identify the compound. Write the equations involved.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type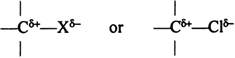

 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain giving reason although haloalkanes are polar in character, yet they are insoluble in water.
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene.
(i) 1-Bromo-1-methyl cyclohexane.
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methyl butane.
(iii) 2, 2, 3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type