 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite structures of different chain isomers of alkanes corresponding to the molecular formula C6H14. Also, write their IUPAC names.
Write structures of different isomeric alkyl groups corresponding to the molecular formula C5H11. Write IUPAC names of alcohols obtained by attachment of -OH groups at different carbons of the chain.
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) (CH3)3 C CH2C(CH3)3
(ii) (CH3)2 C(C2H5)2
(iii) tetra-tert-butyl methane
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite structural formulas of the following compounds:
(i) 3, 4, 4, 5-Tetramethylheptane.
(ii) 2, 5-Dimethylhexane.
Write structures for each of the following compounds. Why are the given names incorrect? Write correct IUPAC names:
(i) 2-Ethylpentane
(ii) 5-Ethyl-3-methylheptane
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow are alkanes formed from:
(i) unsaturated hydrocarbons
(ii) sodium salt of fatty acids?
(i) From unsaturated hydrocarbons: It consist of passing hydrogen gas through alkenes or alkynes in the presence of finely divided nickel at 523 - 573 K. Saturated hydrocarbons are produced.
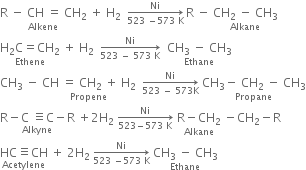
These are known as Sabatier and Senderen's reactions.
Methane can not be prepared by this method.
(ii) From sodium salt of fatty acids. The sodium salt of carboxylic acids on strong heating with soda lime (NaOH + CaO) yield alkanes. The reaction is termed as decarboxylation reaction since it involves the removal of carbon dioxide.


Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer bytaking one example.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type