 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite structures of different chain isomers of alkanes corresponding to the molecular formula C6H14. Also, write their IUPAC names.
Write structures of different isomeric alkyl groups corresponding to the molecular formula C5H11. Write IUPAC names of alcohols obtained by attachment of -OH groups at different carbons of the chain.
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) (CH3)3 C CH2C(CH3)3
(ii) (CH3)2 C(C2H5)2
(iii) tetra-tert-butyl methane
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWrite structural formulas of the following compounds:
(i) 3, 4, 4, 5-Tetramethylheptane.
(ii) 2, 5-Dimethylhexane.
Write structures for each of the following compounds. Why are the given names incorrect? Write correct IUPAC names:
(i) 2-Ethylpentane
(ii) 5-Ethyl-3-methylheptane
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHow are alkanes formed from:
(i) unsaturated hydrocarbons
(ii) sodium salt of fatty acids?
Preparation from alkyl halides. Alkanes can be prepared from alkyl halides by the following methods:
1. By Wurtz’s reaction. It involves the chemical reaction between an alkyl halide and metallic sodium in the presence of dry ether. Two molecules of alkyl halide will react to form higher alkanes.


Methane cannot be prepared by this method.
When we use mixed alkyl halides, for example, methyl bromide and ethyl bromide, more than one product are obtained. 


This reaction is not suitable to prepare pure alkane with an odd number of carbon atoms because of side reactions.
Mechanism of Wurtz’s reaction: Two different mechanisms have been proposed.
(a) Intermediate formation of an organometallic compound:
(b) Intermediate formation of free radical: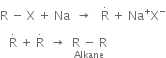
2. By Corey-House reaction: By Corey-House reaction: An alkyl halide is first treated with lithium metal in dry ether to form alkyl lithium. This then reacts with cuprous iodide to yield lithium dialkyl copper and which on subsequent treatment with a suitable alkyl halide gives the desired alkane.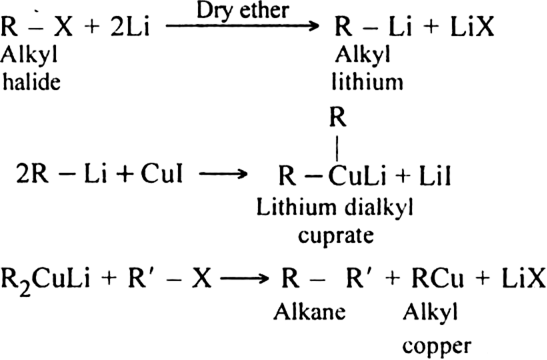
(R and R' may be same or different alkyl groups)
For example: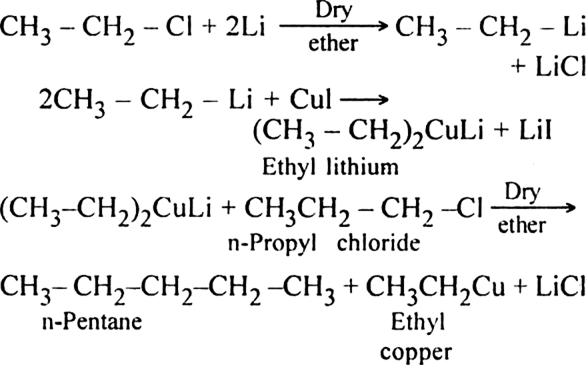
This reaction is very useful for the preparation of both symmetrical and unsymmetrical alkanes.
3. By the reduction of alkyl halides: The reduction of alkyl halide is carried:
(i) With zinc-copper and alcohol or zinc and HCl or zinc and NaOH: Zinc reacts with alcohol to produce nascent hydrogen which brings about reduction.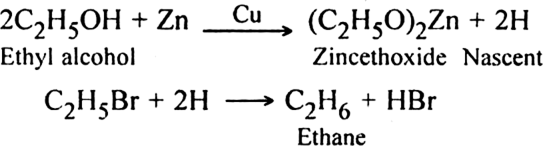
(ii) By catalytic reduction: By using hydrogen gas in the presence of platinum or palladium.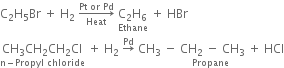
(iii) With red phosphorus and hydrogen iodide: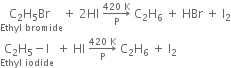
The function of red phosphorus is to combine with iodine to form phosphorus tri-iodide PI3. If it is not done, iodine will react back with an alkane to form alkyl halide.
4. Through the formation of Grignard reagent: Alkyl halides react with dry magnesium metal in the presence of anhydrous ether to form alkyl magnesium halides, also called Grignard reagent.
Grignard reagent can be easily decomposed by water or alcohol to form alkane.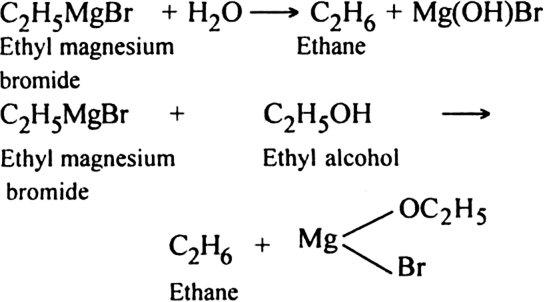
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer bytaking one example.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type