 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeSodium salt of which acid will be needed for the preparation of propane? Write chemical equation for the reaction.
What happens when:
(i) Propyne is heated with H2 in the presence of nickel at 473 K?
(ii) Water is dropped on aluminium carbide?
(iii) Sodium propionate is heated with sodalime?
(iv) Acetic acid is treated with hydroiodic acid in the presence of red phosphorus at 420 K?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) Boiling points of n-alkanes increase regularly with the increase in the number of carbon atoms.
(ii) Branched-chain alkanes have lesser boiling points than the straight chain alkanes.
(i) Alkanes are non-polar molecules and hence are held together by weak Vander Waal’s forces of attraction amongst their molecules. These forces act on the surface of molecules and their magnitude increases with the increase in surface area of the molecules. Thus, with the increase in the number of carbon atoms, the magnitude of Vander Waals forces increases and with that boiling points also increase.
(ii) This is because the branching of the chain makes the molecule more compact and bring the various atoms closer. As a result, the molecular size decreases. This decreases the surface area and hence the magnitude of Vander Waal’s forces (inter-particle forces) and lead to the decrease in boiling point. The boiling points of isomeric alkanes are given below: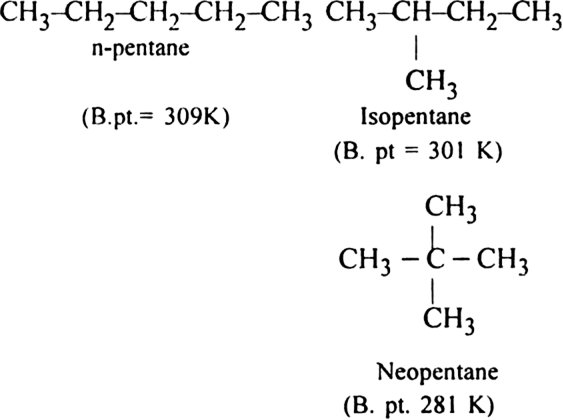
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeAssign reasons for the following:
(i) All C-H bonds in methane are equivalent.
(ii) Alkanes are called paraffins.
Alkanes with even carbon atoms have higher melting points than alkanes with an odd number of carbon atoms.Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhy does the iodination of methane require an oxidising agent while so much reagent is needed in the chlorination and bromination of methane?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type