113.
Explain briefly the process of cracking or pyrolysis.
Cracking: Alkanes, when subjected to high temperature (670-970 K.) in the presence of a catalyst, are decomposed into smaller molecules. This process of breaking down the less volatile higher hydrocarbons into different types of more volatile lower hydrocarbons by the application of heat is called cracking or pyrolysis. The cracking of alkanes involves the cleavage of C-C and C-H bonds. For example,

Pyrolysis of alkanes is supposed to occur by the free radical mechanism. Preparation of oil gas or petrol gas from kerosene oil or petrol involves the principle of pyrolysis. For example, heating to 973K in the presence of Pt, Pd or Ni gives a mixture of heptane and pentene.
Cracking is of two types:
(i) Thermal cracking: It may be carried out in the vapour phase or in the liquid phase. It is difficult to control and gives rise to complex product mixtures.
(ii) Catalytic cracking. It is carried out at a temperature of 670- 820 K using silica and alumina as a catalyst.
Catalytic cracking is useful as it gives gasoline having higher octane number.
The products formed during cracking depends upon:
(i) the structure of starting alkane
(ii) the pressure applied
(iii) use of a catalyst.
519 Views
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
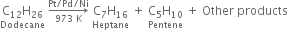
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type