 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeGive IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(a) CH3CH = (CH3)2
(b) CH2 = CH – C ≡ C – CH3
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite structure and IUPAC names of different structural isomers of alkenes corresponding to C5H10.
What is meant by hindered (or restricted) rotation around carbon-carbon double bond? What type of isomerism does it lead to?
What is geometrical isomerism? What is its cause? Give examples.
When the same molecular formula represents two compounds which differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms or groups around carbon-carbon double bond, then such isomers are called geometrical isomers. The phenomenon is called geometrical isomerism.
Cause of geometrical isomerism: Geometrical isomerism is due to the restricted or hindered rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond. Due to the hindered rotation around carbon-carbon double bond, the relative positions of atoms or group attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms get fixed. For example, the molecular formula C2A2B2with the structural formula BAC=CAB represents two geometrical isomers.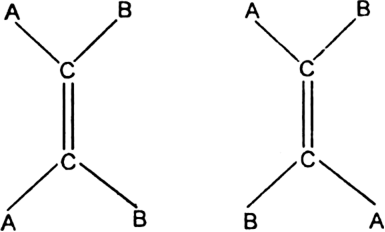
Isomer in which similar atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond is called cis-isomer. The geometrical isomer I represent a cis-isomer. Isomer in which the similar atoms or groups lie on the opposite sides of the double bond is called trans-isomer. The geometrical isomer (ii) represents a trans-isomer. Hence, geometrical isomerism is known as cis-trans isomerism e.g.
(i) But-2-ene exhibits geometrical isomerism.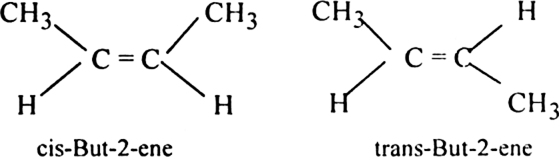
(ii) Hex-3-ene shows geometrical isomerism.
(iii) 1, 2-dichloroethene exhibits geometrical isomerism.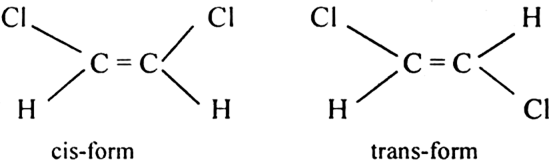
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat are the necessary and sufficient conditions for a compound to exhibit geometrical isomerism ?
Name the various structural isomers possible in C4H8. Which one will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
