 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) Ethyl alcohol is heated in the presence of Al2O3 at 493 K?
(ii) Ethylene dibromide is heated with zinc dust?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the mechanism of the following reaction: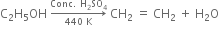
Mechanism of the above reaction involves three steps:
(i) Formation of protonated alcohol. H2SO4 ionises to give H+ ion which attacks the molecule of alcohol to form protonated alcohol.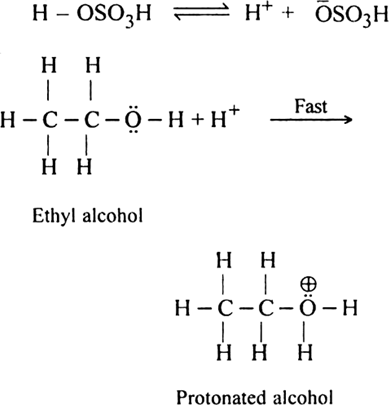
(ii) Formation of the carbocation. Protonated alcohol eliminates a molecule of water to give a carbocation. 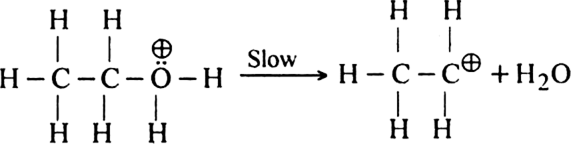
(iii) Formation of ethylene. Carbocation finally loses a proton to hydrogen sulphate ion to form ethylene. 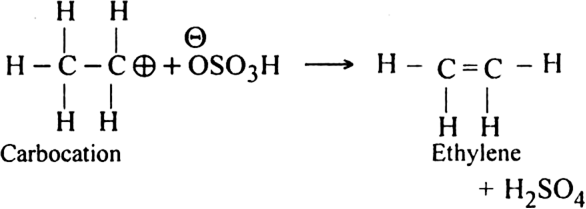
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the mechanism of addition hydrogen acids to symmetrical alkenes. Justify the order of reactivity of halogen acids HI > HBr > HCl.
