 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat happens when:
(i) Ethyl alcohol is heated in the presence of Al2O3 at 493 K?
(ii) Ethylene dibromide is heated with zinc dust?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss the mechanism of addition of bromine to ethylene.
Bromine adds to ethylene at ordinary temperature to form ethylene dibromide. 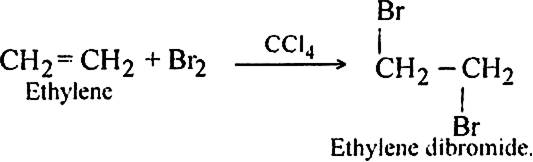
Mechanism: The mechanism of addition of bromine to ethylene is electrophilic in nature and consists of the following steps:
(i) Electromeric effect and electrophilic attack. 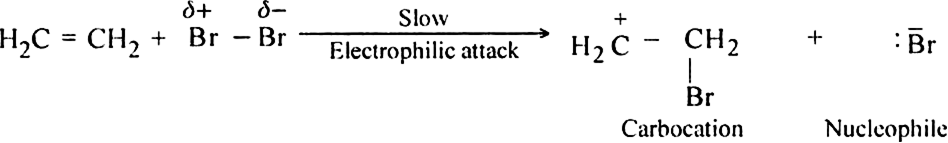
(ii) Attack of the nucleophile: The nucleophile released in the slow step combines with carbocation to give 1, 2-Dibromoethane. 
The above mechanism cannot explain the formation of the trans product. The formation of trans product can only be explained by cyclic halonium ion mechanism which consists of the following steps:
Step I. Formation of cyclic bromonium ion.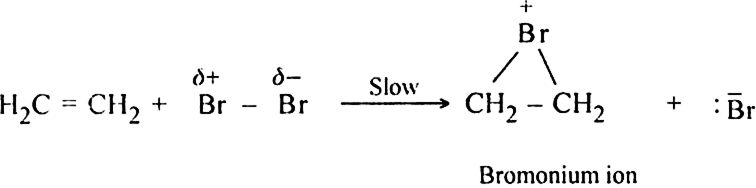
Step II. Formation of the trans product.
The Br- ion attacks one of the carbon atoms of bromonium ion (from the side opposite to that on which positively charged bromine is present) giving rise to the formation of trans addition product. 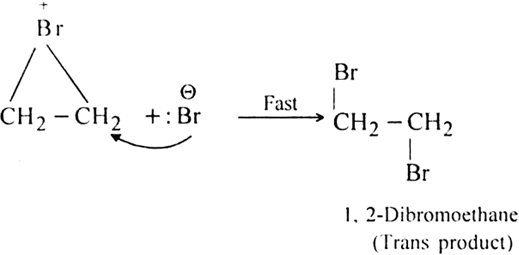
Discuss the mechanism of addition hydrogen acids to symmetrical alkenes. Justify the order of reactivity of halogen acids HI > HBr > HCl.
