 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeFor the following compounds, write structural formulas and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having the number of double or triple bond as indicated:
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type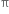 -electrons are more tightly held by the nuclei of carbon atoms in alkyne than in alkene. As a result, the
-electrons are more tightly held by the nuclei of carbon atoms in alkyne than in alkene. As a result, the 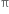 electrons are less easily available for combination with the electrophiles. Hence alkynes are less reactive than alkenes.
electrons are less easily available for combination with the electrophiles. Hence alkynes are less reactive than alkenes.