 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDiscuss in brief the oxidation reactions of alkynes.
Different products are formed depending upon the nature of oxidising agent:
(i) Using cold dilute KMnO4 (Baeyer’s reagent): Alkynes are oxidised by cold dilute KMnO4 to form 1, 2-diketones or carboxylic acids.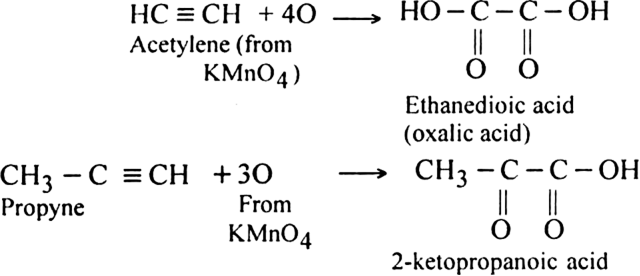
The pink colour of KMnO4 gets discharged. Therefore, this reaction is used as a test for unsaturation in the molecule.
(ii) Using hot KMnO4: When alkynes are treated with hot KMnO4, a triple bond is completely broken forming carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide depending upon the structure of alkyne.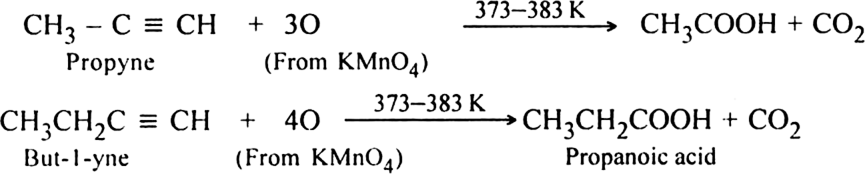
(iii) Oxidation with ozone. The reaction of alkynes with ozone followed by reduction with zinc and water results in the formation of diketones. e.g.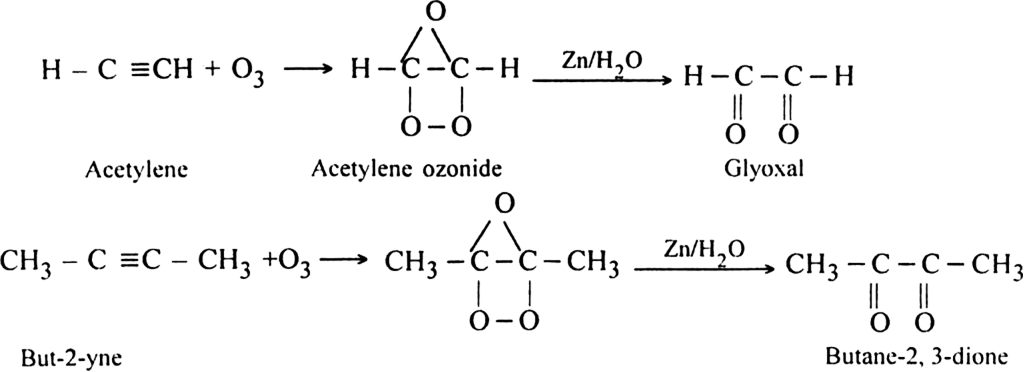
(iv) Combustion: Acetylene and higher alkynes burn when heated with air or oxygen to form CO2 and H2O. The reaction is highly exothermic in nature.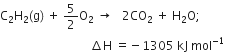
The heat evolved during the reaction is employed as an oxyacetylene flame for welding purposes.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for his behaviour.
Give simple chemical test for the distinction of:
(i) Propyne and propane
(ii) But-1-yne and But-2-yne.
