 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeYou are given samples of ethane, ethene and ethyne in three different containers. How will you distinguish them?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeBenzene ring has three double bonds in it but is still quite stable. Explain.
Or
Why is benzene extra-ordinary stable though it contains three double bonds?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeA resonance may be defined as a phenomenon in which a single compound is supposed to be existing as a hybrid of two or more compounds differing in the distribution of electrons and not of atoms. These different structures of the molecule are known contributing structures or resonating structures or canonical forms. The actual structure that is intermediate between all the contributing structures is called resonance hybrid. Different contributing structures are written by putting a double head arrow ( ↔ ) between them.
Resonance in benzene: Benzene ring has three double bonds in it and is expected to be quite reactive. But benzene is extremely stable. The stability of benzene is explained in terms of resonance. Benzene molecule is a resonance hybrid of the following two main contributing structures: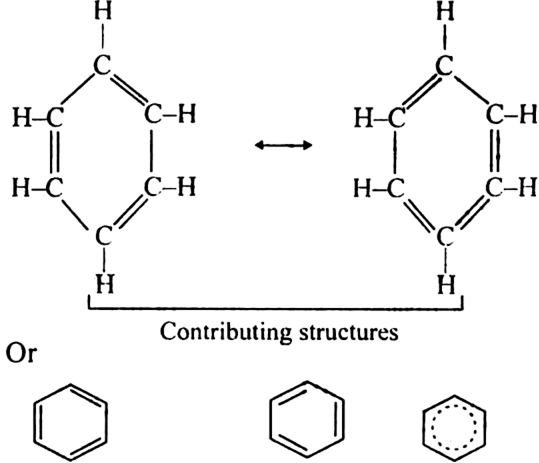
Due to resonance in benzene, the carbon-carbon bonds in benzene acquire an intermediate character of carbon-carbon single and double bonds. As a result, each carbon-carbon bond length in benzene is 139 pm which lies between standard C – C bond length 154 pm and C=C bond length 134 pm.
Effect of resonance: Due to resonance, the  -electron charge in benzene is distributed over a greater area. The density of the charge decreases. As a result, the energy of resonance hybrid also decreases or its stability increases.
-electron charge in benzene is distributed over a greater area. The density of the charge decreases. As a result, the energy of resonance hybrid also decreases or its stability increases.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type