 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeThe compounds possessing aromatic character show the following characteristics:
(i)Â The compounds must be cyclic in nature and have flat planar structure.
(ii)Â Their molecular formulae suggest these compounds to be highly unsaturated due to the presence of one or more double bonds in the ring but they must behave as saturated compounds.
(iii)Â They must resist addition reaction and take part in the electrophilic substitution reactions.
(iv) The molecules have delocalised π electron cloud above and below the plane of the ring.
(v) The most essential criteria for the aromatic character is that the compound must obey Huckel’s rule. According to this rule, a cyclic compound will behave as aromatic compound if it contains (4 n + 2)   electrons, may be 0, 1, 2, 3 etc. Huckel's rule can be applied successfully to polycyclic compounds, annulenes and also other non-benzenoid compounds. For example;
 electrons, may be 0, 1, 2, 3 etc. Huckel's rule can be applied successfully to polycyclic compounds, annulenes and also other non-benzenoid compounds. For example;
(a) Monocyclic systems: Some monocyclic systems having π-electrons (obey Huckel’s rule) possess aromatic character.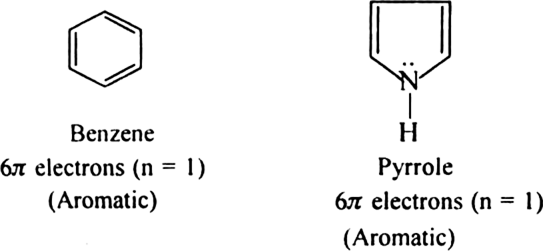
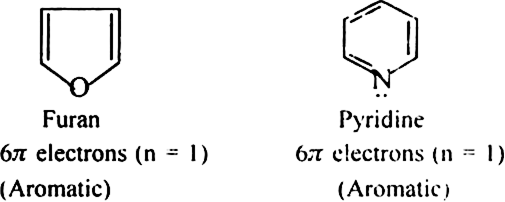
b) Fused ring systems: The polynuclear hydrocarbons such as naphthalene, anthracene and phenanthrene are also aromatic according to Huckel’s rule.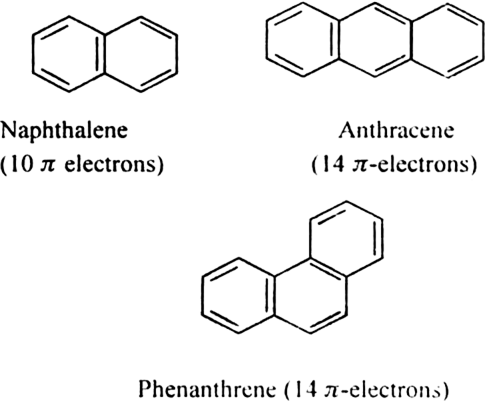
Aromatic ions: Some cyclic ions also exhibit aromatic character. For example.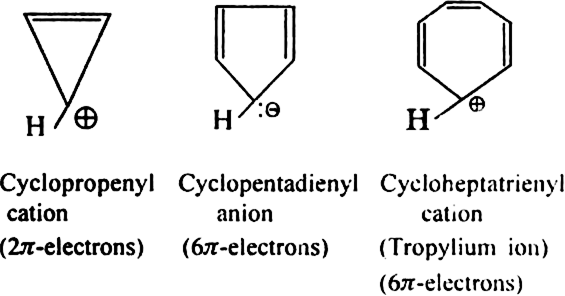
The following compounds are not aromatic: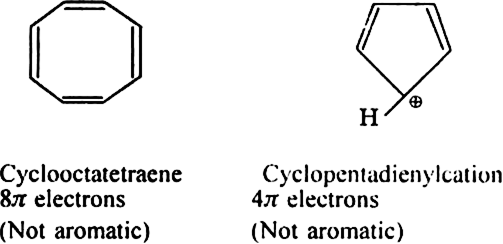
Cycloheptatriene although obeys Huckel’s rule yet it is not aromatic as it is not planar and can not show resonance.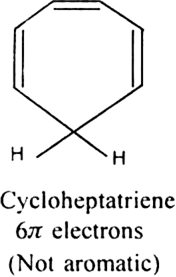
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeArrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give a reason for this behaviour.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBenzene can be conveniently converted into n-propyl benzene by
Friedel-Craft alkylation with n-propyl chloride
Friedel-Craft acylation with propionyl chloride followed by Wolff-Kishner reduction
Friedel-Craft acylation with propionyl chloride followed by catalytic hydrogenation
Friedel-Craft acylation with propionyl chloride followed by reduction with LiAlH4
At 300 K and 1 atm, 15 mL of a gaseous hydrocarbon requires 375 mL air containing 20% O2 by volume for complete combustion. After combustion the gases occupy 330 mL. Assuming that the water formed is in liquid form and the volumes were measured at the same temperature and pressure, the formula of the hydrocarbon is:
C3H8
C4H8
C4H12
C4H12
