 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type| Potassium chloride (KCl) | Aluminium (III) chloride (AlCl3) |
1. Normal water. KCl being a salt of strong base and strong acid does not undergo hydrolysis in normal water but simply dissociates to give K+ (aq) and Cl- (aq) ions.  |
1. Normal water. AlCl3 being a salt of weak base and strong acid, it undergoes hydrolysis in normal water. |
| 2. Acidified water and alkaline water. Since aqueous solution of KCl is neutral, therefore in acidified water and alkaline water, the ions will remain as such i.e. do not react further. | 2. In acidic water. H+ ions react with Al(OH)3 to form Al3+ (aq) ions and H2O. Hence in acidic water, AlCl3 exists as Al3+(aq) and Cl-(aq) ions. 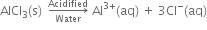 |
3. In alkaline water.  reacts to form soluble tetrahydroxaluminate complex or meta-aluminate ion. reacts to form soluble tetrahydroxaluminate complex or meta-aluminate ion. 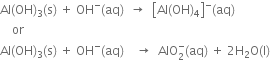 |
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow will you prepare a sample of temporary hard water from lime water? Write equation for the reactions involved.
