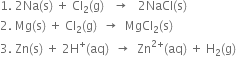Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeShow that oxidation cannot occur without reduction.
Or
Show that oxidation and reduction go side by side.

 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type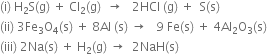
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat are the changes which take place when a redox reaction is carried in a beaker? Explain with the help of a suitable example.
Or
Explain the redox reaction
occurring in a beaker.
What do you mean by redox reactions in aqueous solutions? Give examples.
A large number of redox reactions proceed slowly in aqueous solutions. Each redox reaction can be considered as a sum of two half reactions-one involving oxidation called oxidation half reaction and the other involving reduction called reduction half reaction. For example;
(a) Let us consider the oxidation of aqueous potassium iodide by hydrogen peroxide. This reaction can be divided into two half reactions.
Supplying the required number of spectator ions, the balanced redox equation is

Note. The ions which do not part in any reaction but are simply added to balance the charge are called spectator ions.
(b) Consider the oxidation of aqueous ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate by aqueous acidified KMnO4 solution.
Supplying the required spectator ions, the complete balanced redox equation is
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type