 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhy do the following reactions proceed differently?
Pb3O4 +8HCl --->3PbCl2 +Cl2 +4H2O
Pb3O4 +4HNO3 --->2Pb(NO3)2 +PbO2 +2H2O
Consider the reaction:![]()
![]()
Why does the same reductant—thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type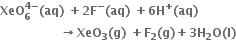
conclusion about the compound Na4XeO6 (of which XeO64– is a part) can be drawn from the reaction ?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type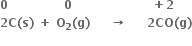
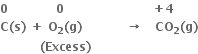
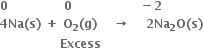
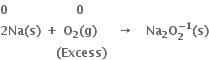

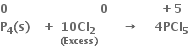
Consider the reactions:
Why is it more appropriate to write these reactions as:
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the above (a) and (b) redox reactions.
