 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
The Mn3+ ions is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2 and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypePermanganate (VII) ion,  in basic solution oxidises iodide ion, I- to produce molecule iodine (I2) and manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2). Write a balanced ionic equation to represent redox reaction.
in basic solution oxidises iodide ion, I- to produce molecule iodine (I2) and manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2). Write a balanced ionic equation to represent redox reaction.
Balance the following equations in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number method:
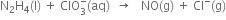
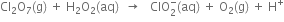
(A) Ion-electron method:
1. Write the oxidation and reduction half-reaction by observing the changes in oxidation numbers.
Oxidiation half reaction:
-1 0

Reduction half-reaction:
+7 +3

2. Balancing the oxidation half reaction
(i) Add 2 electrons towards R.H.S. to balance the charges

(ii) Add 2 OH- ions towards L.H.S to balance the charges

(iii) Balance O atoms by adding two H2O molecules towards H

3. Balancing the reduction half reaction


4. Multiply balanced oxidation half-reaction by 4 and add it to the balanced reduction half-reaction.
(B) Oxidation number method
(i) The skeleton equation along with oxidation number of each atom is
+7 -2 +1 -1 +3 0
(ii) The ON of O atom increases by 1 per atom while that of CI decreases by 4 per atom.
Thus Cl2O7(g) acts as an oxidising agent while H2O2(aq) as the reducing agent
Total increase in O.N. of H2O2 = 2 X 1=2
Total decrease in O.N. of Cl2O7 = 4 x 2 = 8
(iii) Equalise the increase/decrease in O.N. by multiplying H2O2 and O2 by 4.
(iv) Balance Cl atoms by multiplying 

(v) Balance O atoms by adding three  towards R.H.S.
towards R.H.S.

(vi) Balance H atoms by adding two  towards R.H.S. and two OH- towards L.H.S.
towards R.H.S. and two OH- towards L.H.S.
This is the balanced redox equation.
