 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeHeptane and Octane form an ideal solution at 373 K. The vapour pressures of the pure liquids at this temperature are 105.2 K Pa and 46.8 K Pa respectively. If the solution contains 25 g of heptane and 28.5 g of octane, calculate
(i) Vapour pressure exerted by heptane.
(ii) Vapour pressure exerted by solution.
(iii) Mole fraction of octane in the vapour phase.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Measurement of Osmotic Pressure. Different methods are employed for the measurement of osmotic pressure in the laboratory but Berkley and Hartley's method gives the best results. The apparatus consists of a porous pot containing copper ferrocyanide deposited in its wall (acts as semi-permeable membrane) and fitted into a bronze cylinder to which is fitted a piston and a pressure gauge (to read the applied pressure).
The pot is fitted with a capillary indicator on left and water reservoir on right. Pot is filled with water while the cylinder is filled with a solution whose osmotic pressure is to be measured. Water tends to pass into the solution through the semipermeable membrane with the result that the water level in the indicator falls down. External pressure is now applied with piston so as to maintain a constant level in the indicator. This external pressure is osmotic pressure.
If the membrane used was a slightly, leaky, then the measured valued of osmotic pressure will not be definite.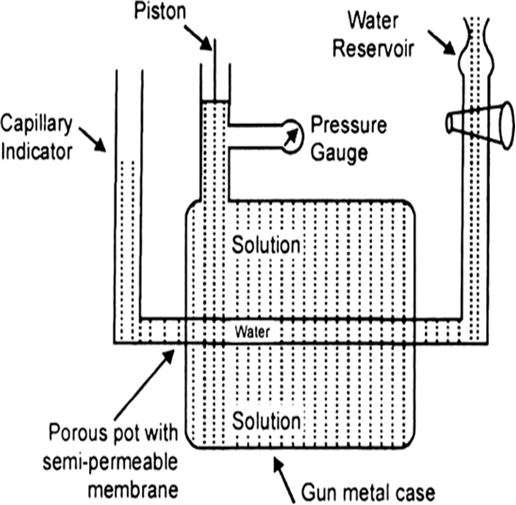
Fig. Berkley and Hartley's apparatus.
(b) 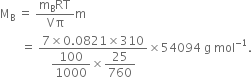
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type