 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeDensity of a gas is found to be 5.46 g/dm3 at 7°C at 2 bar pressure. What will be its density at STP?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIf the density of a gas at the sea level at 0° is 1·29 kg m–3, what is the molar mass? (Assume that pressure is equal to 1 bar).
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type34.05 mL of phosphorus vapours weighs 0.0625 g at 546°C and 0·1 bar pressure. what is the molar mass of phosphorus?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type2.9 g of a gas at 95°C occupied the same volume as 0·184g of hydrogen at 17°C at the same pressure. What is the molar mass of the gas?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeCalculate the mass of methane in a 9L cylinder at 16 bar and 27°C. (R = 0·08L bar K–1 mol–1).
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeTwo flasks A and B have equal volumes. Flask A contains H2 and is maintained at 300K while the flask B contains an equal mass of CH4 gas and is maintained at 600K. In which flask is the pressure greater? How many times ?
Pressure of 1g of an ideal gas A at 27° C is found to be 2 bar. When 2g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at same temperature the pressure becomes 3 bar. Find a relationship between their molecular masses.
Pay load is defined as the difference between the mass of displaced air and the mass of the balloon. Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled With helium at 1·66 bar at 27°C. (Density of air = 1·2 kg m-3 and R = 0·083 bar dm3 K–1 mo1–1).
State and explain Dalton's law of partial pressure ?
It states,'If two or more gases, which do not react chemically, are present together in an enclosed space, the total pressure exerted by the gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of partial pressures which each gas would exert if present alone in that space at the same temperature.'
Mathematically, Ptotal = p1 + p2 + p3 + .... where Ptotal = total pressure exerted by the mixture in a given volume (V) at a given temperature (T)
p1,p2,p3 .... = partial pressure exerted by each
gas. 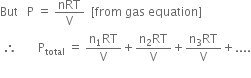

Here X1, X2 ..... are mole fractions of respective gases.
The partial pressure of a gas in a mixture is equal to the mole fraction of the gas multiplied by the total pressure exerted by the gaseous mixture.
