 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow is Dalton's law of partial pressures useful in calculating the pressure of a dry gas?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type300 mL of a gas A at a pressure of 600 mm is mixed with 200mL of another gas B at a pressure of 700 mm in a vessel of 2-litre capacity. What will be the total pressure of the resulting mixture, if the temperature is kept constant?
What will be the pressure of the gaseous mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of dioxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in a 1L vessel at 27°C?
Weight of oxygen = 12 g
Molar mass of oxygen = 32g mol-1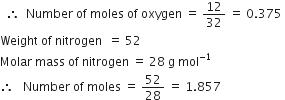
(a) Partial pressure of oxygen gas:
According to general gas equation,
PV = nRT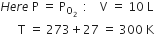
Substituting the value.
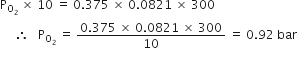
b) The partial pressure of nitrogen gas: According to the general gas equation.
PV = nRT
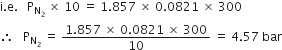
(c) Total pressure of the gaseous mixture : According to Dalton’s law of partial pressure,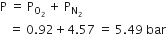
A neon-dioxygen mixture contains 70.6 g dioxygen and 167·5 g neon. If pressure of the mixture of gases in the cylinder is 25 bar, what is the partial pressure of dioxygen and neon in the mixture?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA mixture of dihydrogen and dioxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen. Calculate the partial pressure of dihydrogen.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeCalculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8g of dioxygen and 4g of dihydrogen confined in a vessel of 1 dm3 at 27°C. R = 0·083 bar dm3 k–1 mol–1.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type