 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeHow is Dalton's law of partial pressures useful in calculating the pressure of a dry gas?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type300 mL of a gas A at a pressure of 600 mm is mixed with 200mL of another gas B at a pressure of 700 mm in a vessel of 2-litre capacity. What will be the total pressure of the resulting mixture, if the temperature is kept constant?
What will be the pressure of the gaseous mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of dioxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in a 1L vessel at 27°C?
A neon-dioxygen mixture contains 70.6 g dioxygen and 167·5 g neon. If pressure of the mixture of gases in the cylinder is 25 bar, what is the partial pressure of dioxygen and neon in the mixture?
Weight of dioxygen (O2) = 70.6 g
Molar mass of dioxygen = 32 g mol-1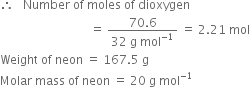
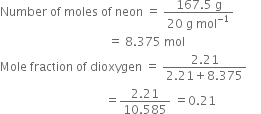
Mole fraction of neon

We know,
Partial pressure of a gas = Mole fraction x Total pressure
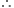 Partial pressure of a gas = Mole fraction x total pressure
Partial pressure of a gas = Mole fraction x total pressure
= 0.21 x 25 bar = 5.25 bar
Partial pressure of neon = 0.79 x 25 bar = 19.75 bar
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA mixture of dihydrogen and dioxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of dihydrogen. Calculate the partial pressure of dihydrogen.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeCalculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8g of dioxygen and 4g of dihydrogen confined in a vessel of 1 dm3 at 27°C. R = 0·083 bar dm3 k–1 mol–1.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type