 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWrite a short note on distribution of velocities of gas molecules.
We know that molecules in a gas go on colliding with each other and hence their velocities go on changing though the average velocity remains unchanged. After the collision, the faster molecule slows down and slower molecule speeds up. The collisions are very rapid (many collisions per second) and hence, it is not possible to find the velocity of any single molecule. However, there must be a fraction of the total number of molecules that has a particular velocity at any time. The distribution of velocities amongst the gaseous molecules i.e. at a given instant how many molecules are moving with a particular speed was calculated by Maxwell and Boltzmann using the laws of probability. The fraction of molecules (∆N/N) possessing a particular velocity is taken on the Y-axis and the velocity on the X-axis. The curve obtained is shown in the figure. It is called ‘normal distribution curve of molecular velocities’.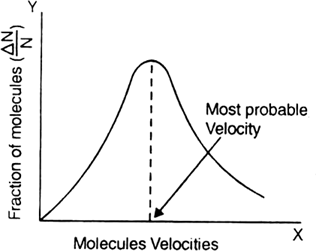
The graph supplies the following information:
(i) The area under the curve gives the total number of molecules.
(ii) A very small fraction of molecules has very low (close to zero) velocities.
(iii) The fraction of molecules having higher and higher velocities keep on increasing with the increase in velocity, reaches a peak value and then starts decreasing for very high velocity. Once again, a very small fraction of molecules has very high velocities.
(iv) The maximum fraction of molecules possesses a velocity corresponding to the peak of the curve. This velocity is termed as most probable velocity (a). Thus, most probable velocity may be defined as the velocity possessed by the maximum fraction of molecules at a given temperature.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeEven though carbon dioxide is heavier than air, it does not form the lower layer, Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat are the faulty assumptions in the kinetic theory of gases which are responsible for deviations from ideal behaviour of gases?
What modifications were applied by Vander Waal to overcome the deviations of the gases from ideal gas behaviour?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the significance of the Vander Waal's constants? Write its units for Vander Waal's constants.
