135.
What is compressibility factor? What is its value for ideal gas and real gas?
Compressibility factor: The deviation of real gases from ideal behaviour can be studied by plotting a graph between  The quantity
The quantity  is called compressibility factor and is denoted by Z.
is called compressibility factor and is denoted by Z.

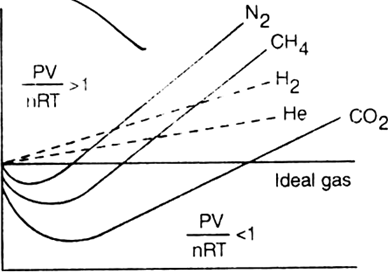
For an ideal gas, Z = 1 under all conditions of temperature and pressure.
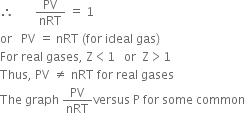
gases such as H2, N2, CH4 and CO2 supplies the following information:
(i) Z = 1, for an ideal gas.
(ii) Z < 1, it is called negative deviation. It means that the gas is more compressible than expected from ideal behaviour.
(iii) If Z > 1, it is called positive deviation. It means that the gas is less compressible than expected from ideal behaviour.
It may be noted that:
(a) For N
2, CH
4 and CO
2, Z < 1 at low pressure and Z > 1 at high pressures. This means that these gases are more compressible at low pressures and less compressible at high pressures than expected from ideal behaviour.
(b) For H
2 and He, Z > 1 at low and high pressures. This means that these gases are less compressible than expected from ideal behaviour at all pressures.
(c) At high-pressure Z shows a large deviation from ideal behaviour. However, at very low-pressure Z is nearly equal to 1.
(d) It may also be noted that the deviations decrease with the increase in temperature.
Thus, the real gases behave in a nearly ideal manner only at low pressures and high temperatures.
569 Views
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type The quantity
The quantity  is called compressibility factor and is denoted by Z.
is called compressibility factor and is denoted by Z.

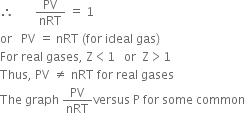
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type