 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeEven though carbon dioxide is heavier than air, it does not form the lower layer, Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat are the faulty assumptions in the kinetic theory of gases which are responsible for deviations from ideal behaviour of gases?
What modifications were applied by Vander Waal to overcome the deviations of the gases from ideal gas behaviour?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeDerive an expression for the Vander Waal's equation of state.
Vander Waal in 1873, modified the general gas equation (PV = nRT) by introducing two correction terms:
(i) Volume correction. He pointed out that for real gases the volume of the gas molecules is not to be neglected in comparison to the total volume of the gas. This means that the molecules are not free to move in the whole of volume V but the free volume is less than the observed volume. In other words, the ideal volume of the gas is less than the observed volume. Vander Waal suggested that
Videal = (V – b) for one mole
where b is the correction term known as co-volume or excluded volume. It is related (not equal) to the actual volume of gas molecules. It has been found that b is about four times the actual volume of the gas molecules.
For n moles of a gas,
Videal = (V – nb)
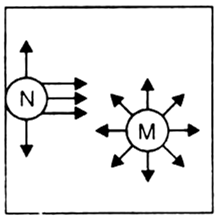
(ii) Pressure correction. There is an attractive force of attraction between molecules of a gas.
A molecule (M) in the interior of the container is surrounded uniformly on all sides by other molecules, so there is no net force of attraction on it.
But when a molecule (N) is about to strike the wall of the container, the molecules are present only on one side of it will attract the striking molecule and pull it back. Thus, the molecule strikes the wall with a lesser force than it would have done if there were no attractive forces. Therefore, the observed pressure is less than the ideal pressure. Consequently, some correction factor must, therefore, be added to the observed pressure in order to calculate ideal pressure.

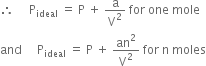
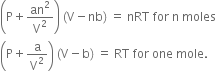
What is the significance of the Vander Waal's constants? Write its units for Vander Waal's constants.
