Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain what is meant by 'critical phenomenon'? What are 'critical constants' of a gas?
Describe briefly the Isotherm of Carbon dioxide.
Or
Briefly describe the Isotherm of Carbon dioxide as studied by Andrews.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeOn the basis of kinetic molecular theory of liquids, how can you explain the following properties of liquids:
(i) Volume (ii) Density
(iii) Compressibility (iv) Diffusion?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
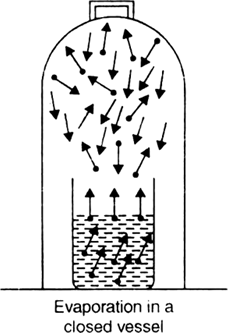
Long Answer TypeExplain briefly the term "vapour pressure" . What are the factors on which vapour pressure of a liquid depends?