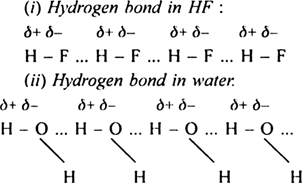Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeExplain the following:
(i) Drops of liquid assume a spherical shape.
(ii) The level of mercury in a capillary tube is lower than the level outside when a capillary tube is inserted in mercury.
Liquid that wets glass rises in a capillary tube or oil rises in the wick of an oil Jamp. Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the following:
(i) The boiling point of water (373 K) is abnormally high when compared to that of H2S (211·2K).
(ii) Liquids like ether and acetone are kept in cool places.
(iii) Tea or coffee is sipped from a saucer when it is quite hot.
Explain briefly the term viscosity. Define coefficient of viscosity. What are its units?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhich one in each of the following pairs is more viscous?
(i) Coconut oil, castor oil
(ii) glyercine, kerosene
(iii) soft drink, aerated water (soda water)?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is the effect of temperature on:
(i) density
(ii) surface tension
(iii) viscosity
(iv) the vapour pressure of a liquid?
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeWhat is the effect of pressure on:
(i) volume
(ii) boiling point
(iii) viscosity of a liquid?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA hydrogen bond is defined as the weak electronic force of attraction which exists between the covalently bonded hydrogen of one molecule and highly electronegative atom of another molecule. Hydrogen bond has a strength of the order of 10 – 100 kJ mol–1as compared to another covalent bond which has a strength of the order of 200 – 400 kJ mol–1. A hydrogen bond is denoted by dotted lines (.....). The hydrogen bonding in hydrogen fluoride is represented as:![]()
Cause for the formation of hydrogen bond: Whenever a hydrogen atom is attached to a highly electronegative atom (for example, N, O, F), the shared pair of electrons between the two atoms is attracted towards the more electronegative atom. Consequently, the highly electronegative atom acquires a partial negative charge (δ–) while the hydrogen atom acquires a partial positive charge (δ+). The partial negatively charged atom of one molecule tends to attract partial positive hydrogen atom of the other molecule. This weak electrostatic attraction constitutes hydrogen bond. For example.