 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Which will absorb more gas, a lump of charcoal or its powder and why?
(b) Describe the preparation of the following colloidal solutions. Name the method used in each case (i) silver sol, (ii) sulphur sol.
Explain What is observed when:
(a) A beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution of As2S3
(b) An electrolyte (NaCl) is added to ferric hydroxide sol.
(c) An electric current is passed through a colloidal solution.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeIllustrate with example:
(i) Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols.
(ii) Multimolecular and macromolecular colloids.
(iii) Homogeneous and Heterogeneous catalysis.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeThe process of Adsorption is an Exothermic Reaction. Thus according to Le-chatlier’s Principle, the magnitude of adsorption should increase with decrease in temperature. Infact it is found to be so in case of physical adsorption because vanderwaal’s forces are strong at low temperatures. However, the chemisorption first increases with rise in temperature and then starts decreasing. The initial increase shows that like chemical reactions, chemisorption also needs activation energy.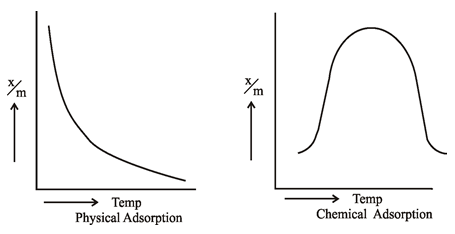
If a plot is drawn between amount of gas adsorbed (x/m) and temperature at constant equilibrium pressure, then curve obtained for physical adsorption shows there is a regular decrease in adsorption with temperature rise. While for chemisorption it first increases and then shows regular decrease. Such curves are known as Adsorption Isobars.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type